Shear stress is defined as the force per unit area acting parallel to the plane of a material. It measures how much force causes a material to slide or shear along a particular plane. The most common application of shear stress analysis in CNC machining involves understanding how different parts behave under various operational forces, ensuring they do not fail during use.
Shear Stress (τ): It is expressed by the formula:
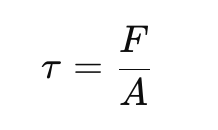
where:τ=F/A
- (τ ) = shear stress (measured in pascals or psi)
- ( F ) = applied force (measured in newtons or pounds-force)
- ( A ) = area over which the force is applied (measured in square meters or square inches)
Shear stress is crucial because many mechanical failures, such as material fractures and joint separations, occur due to shear forces. For CNC-machined components, understanding shear stress helps in designing parts that are resilient and can handle the loads they are exposed to during operation.
Specific reference:How to Use Shear Stress Formula in CNC Design and Production - Want.net